Duqu malware attack exploited a zero-day vulnerability in the Windows kernel, according to security researchers tracking the Stuxnet-like cyber-surveillance Trojan. The vulnerability has since been reported to Microsoft and Microsoft is working on a fix for the kernel vulnerability right now.
Researchers at the Laboratory of Cryptography and System Security (CrySyS) in Hungary confirmed the existence of the zero-day vulnerability and exploit in a brief note posted to its web site.
Researchers at the Laboratory of Cryptography and System Security (CrySyS) in Hungary confirmed the existence of the zero-day vulnerability and exploit in a brief note posted to its web site.
Our lab, the Laboratory of Cryptography and System Security (CrySyS) pursued the analysis of the Duqu malware and as a result of our investigation, we identified a dropper file with an MS 0-day kernel exploit inside. We immediately provided competent organizations with the necessary information such that they can take appropriate steps for the protection of the users.
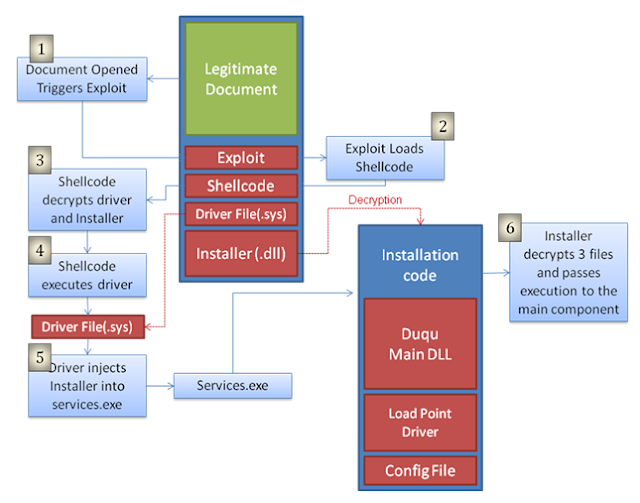
The installer file is a Microsoft Word document (.doc) that exploits a previously unknown kernel vulnerability that allows code execution. We contacted Microsoft regarding the vulnerability and they're working diligently towards issuing a patch and advisory. When the file is opened, malicious code executes and installs the main Duqu binaries. The chart below explains how the exploit in the Word document file eventually leads to the installation of Duqu.
Other security vendors have reported infections in the following countries: • Austria • Hungary • Indonesia • United Kingdom • Iran - infections different from those observed by Symantec.
"Microsoft is collaborating with our partners to provide protections for a vulnerability used in targeted attempts to infect computers with the Duqu malware. We are working diligently to address this issue and will release a security update for customers through our security bulletin process," Jerry Bryant, group manager of response communications in Microsoft's Trustworthy Computing group said in a statement.
You can find Symantec updated whitepaper (version 1.3) here. Key updates in the Symantec whitepaper include:
• Attackers can spread Duqu to computers in secure zones and control them through a peer-to-peer C&C protocol
• Six possible organizations in eight countries have confirmed infections
• A new C&C server (77.241.93.160) hosted in Belgium was discovered and has been shut down.
[Source]
Found this article interesting? Follow us on Google News, Twitter and LinkedIn to read more exclusive content we post.